Cookie Policy: This site uses cookies to improve your experience. You can find out more about our use of cookies in our Privacy Policy. By continuing to browse this site you agree to our use of cookies.
Innaxon
Lipodisq™ Control Sterile Solution
244
CHF
CHF 244.00
In stock
IAX-700-100-L0011 mlCHF 244.00

| Product Details | |
|---|---|
| Synonyms | Detergent-free Nano-formulation made of Styrene-maleic Acid Lipid Particles (SMALP) |
| Product Type | Chemical |
| Properties | |
| Appearance | Colourless clear aqueous solution. |
| Solubility | Soluble in water, PBS, Tris and other physiological solutions as formulated in a proprietary, thermostable, aqueous lipid nanoparticulate formulation (Lipodisq). |
| Reconstitution | Avoid the use of buffers with divalent ions such as Ca or Mg or pH <6.5 or >8.0, which can cause particle instability. |
| Formulation | Liquid, detergent-free discoidal nano-formulation made of styrene-maleic acid lipid particles (SMALP), lecithin and sterile water. |
| Biological Activity |
|
| Declaration | Manufactured by Innaxon. |
| Other Product Data |
Click here for Original Manufacturer Product Datasheet: Our product description may differ slightly from the original manufacturer's product datasheet. Lipodisq™ technology is covered by one or more of the following patents owned by Malvern Cosmeceutics Limited: AU2006253886, CA2611144, CN101184473B, EP1890675, GB2426703, IN261468, JP5142898, US8623414 and WO/2021/005340A1 pending. The purchaser is licensed under those patents to use these assemblies for the purpose of research and development only, but not for the purpose of delivery of agents for clinical use to humans or veterinary use to animals for therapeutic, diagnostic or prophylactic purposes, which uses are specifically prohibited. |
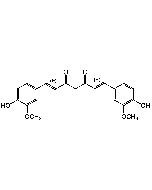
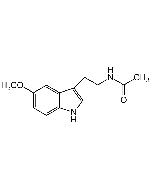
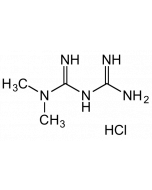
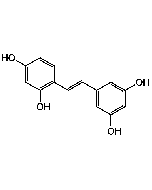
| Smiles | |
| Shipping and Handling | |
| Shipping | AMBIENT |
| Short Term Storage | +4°C |
| Long Term Storage | +4°C |
| Handling Advice |
Keep sterile. Avoid skin and eye contact. |
| Use/Stability | Stable for at least 1 year after receipt when stored at +4°C. |
| Documents | |
| MSDS | Inquire |
| Product Specification Sheet | |
| Datasheet |
 Download PDF Download PDF |
Description
- A nanoparticle (11-40nm) drug delivery system comprising a discoidal phospholipid bilayer membrane stabilized by a chaperone molecule annulus.
- Internal properties of the phospholipid membrane support the disposition and stabilization of drug molecule candidates and preserve the native conformation of membrane molecules.
- The resulting encapsulated actives are rendered water-soluble and specialized for intra-cellular penetration/delivery via endosomal uptake mechanisms.
- Lipodisq™ solutions show a good safety profile and are suitable for in vitro and in vivo investigations.
Product References
- Characterizing the structure of lipodisq nanoparticles for membrane protein spectroscopic studies: R. Zhang, et al.; Biochim. Biophys. Acta. 1848, 329 (2015)
- Nano-size uni-lamellar lipodisq improved in situ auto-phosphorylation analysis of E. coli tyrosine kinase using (19)F nuclear magnetic resonance: D. Li, et al.; Protein Cell 6, 229 (2015)
- Reconstitution of membrane proteins: a GPCR as an example: A.D. Goddard, et al.; Methods Enzymol. 556, 405 (2015)
- The styrene–maleic acid copolymer: a versatile tool in membrane research: J.M. Doerr, et al.; Eur. Biophys. J. 45, 3 (2016)
- From polymer chemistry to structural biology: The development of SMA and related amphipathic polymers for membrane protein extraction and solubilization: J.F. Bada Juarez, et al.; Chem. Phys. Lipids. 221, 167 (2019)
- Effects of charged lipids on the physicochemical and biological properties of lipid–styrene maleic acid copolymer discoidal particles:M. Tanakaa, et al.; Biochim. Biophys. Acta. Biomembr. 1862, 183209 (2020)
- Physicochemical Characterization, Toxicity and In Vivo Biodistribution Studies of a Discoidal, Lipid-Based Drug Delivery Vehicle: Lipodisq Nanoparticles Containing Doxorubicin: M.L. Torgersen, et al.; J. Biomed. Nanotechnol. 16, 41 (2020)
- Understanding the Structural Pathways for Lipid Nanodisc Formation: How Styrene Maleic Acid Copolymers Induce Membrane Fracture and Disc Formation: V.A. Bjornestad, et al.; Langmuir 37, 6178 (2021)
- Applications of Synthetic Polymer Discoidal Lipid Nanoparticles to Biomedical Research: M. Tanaka; Chem. Pharm. Bull. 70, 507 (2022)
- Mechanisms of Formation, Structure, and Dynamics of Lipoprotein Discs Stabilized by Amphiphilic Copolymers: A Comprehensive Review: P.S. Orekhov, et al.; Nanomaterials 12, 361 (2022)